Safety and Health in Management
MEMBERS

Monday, 2 May 2016
Monday, 25 April 2016
Important to have a health and safety management system
- Economic Reasons
Besides reducing costs, effective safety and health management promotes business efficiency. Thousands of work-related accidents, resulting in more than three days off work are reported to the Health and Safety Authority each year. Work-related diseases and ill-health are more difficult to measure due to their long latency period but result in excess of one million days lost at work each year. These accident and ill-health cases are due to failures and deficiencies in the occupational safety and health management in organizations.
- Legal Reasons
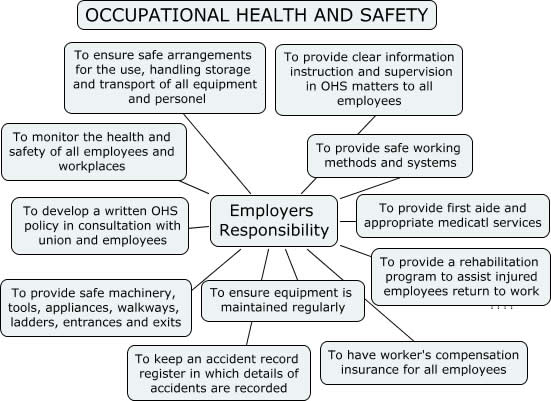
The Safety, Health and Welfare at Work Act 2005 (the 2005 Act) requires all duty holders to ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, the safety, health and welfare of workers and members of the public and to manage and conduct all work activities in such a way as to ensure their safety, health and welfare. This requires all who have this legal responsibility to be proactive in managing their safety, health and welfare responsibilities and deal with them in a systematic way. This section should help organization to improve their safety and health performance by providing advice on how safety and health should be managed, and in the process help them to comply with their legal requirements.
- Moral and Ethical Reasons
The proactive management of safety and health in the workplace helps organization prevent injuries and ill-health at work. This guidance should help organization reduce the personal loss caused as a result of accidents and ill-health at work
Reason makes a successful system
I. Make a commitment
Put as much energy into your commitment to safety and health as you put into any other important part of your business. Make sure to include workplace safety and health in your business plan and integrate it into all facets of the business.
II. Involve employees
In a safe and healthy workplace, employees have a stake in the success of the program --- safety and health is everyone's responsibility. Actively encourage employee involvement if you want your program to succeed. Hold people accountable and makes sure everyone does their part.
II. Identify and control hazards
Before you can control hazards you need to know what the hazards are
IV. Comply with regulations
Employers must identify the OSHA regulations that apply in their workplaces and comply with them.
V. Train Employees
Train personnel about the hazards they may be exposed to at work and how to protect themselves. Keep records of all training
Monday, 11 April 2016
Sunday, 10 April 2016
How To Ensure Workplace Safety
Step 1
Assess the risks specific to the workplace. Each workplace holds its own risks and dangers based on the nature of the work, so a thorough assessment of the surroundings is key.
Step 2
Create safety policies and procedures that address the identified risks for the workplace. Ensure that all employees receive training and have access to these policies and procedures.
Step 3
Conduct background checks on potential employees to check for red flags that could threaten the safety of other employees.
Step 4
Inspect the physical space of the workplace to identify dangers. Ensure that all lighting and safety equipment remain in good working order. Make necessary repairs to the facilities immediately.
Step 5
Create a plan of action in case of an emergency. Consider the types of emergencies that may threaten the workplace. Practice the emergency response with the staff to ensure everyone understands the procedures.
Step 6
Establish a procedure for visitors in the workplace. Restricting access without an escort, checking identification and requiring visitors to sign in are typical procedures.
Step 7
Establish an environment that encourages open communication. Initiate a zero-tolerance policy for violence and discrimination to ensure all employees feel safe and free to express their opinions.
10 Most Common Workplace Accidents
- Overexertion – This includes injuries related to pulling, lifting, pushing, holding, carrying, and throwing activities at work. Overexertion has consistently been a number one workplace injury among the surveys and statistics.
- Fall on Same Level Surfaces – This pertains to falls on wet and slippery office floors. Other related examples are falls and slips especially by elderly people on snow covered pathways on their way to work.
- Fall to Lower Level – This type of fall happens from an elevated area such as roofs, ladders, and stairways.
- Bodily Reaction – These are injuries caused by slipping and tripping without falling.
- Struck by Object – Objects that fall from shelves or dropped by another person. These can cause very serious injuries.
- Struck against an Object – This happens when a person accidentally runs into concrete objects such as walls, doors, cabinets, glass windows, table, chairs etc.
- Highway Incident – Transportation used for business purposes such as trucks and cars may be involved in an automobile accident just like any regular traveler.
- Caught In/ Compressed By – This type of injury usually occurs in a factory where large and dangerous machinery is used. Sometimes little or no precaution in its usage may endanger the safety of its operators. Exposure to extreme temperature is also an example of this workplace injury.
- Repetitive Motion – This type of workplace injury is one of those less obvious but definitely harmful ones in the long run. Repetitive motions such as typing and using the computer 24/7 can strain muscles and tendons causing back pain, vision problems, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Assaults and Violent Acts – Attacks caused by office politics and other arguments have led to serious physical injuries.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)